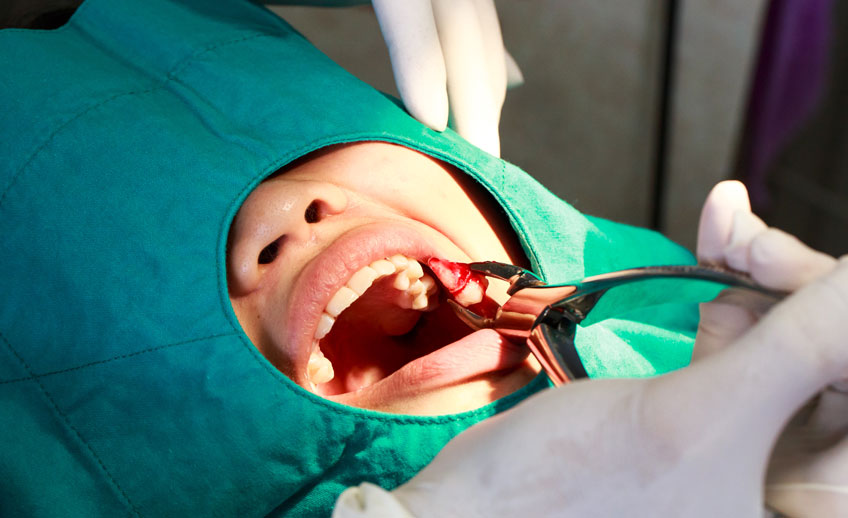
Unlike normal/ conventional extractions that involve the removal of tooth by conservative means; a surgical extraction is more invasive in nature.
In cases where a tooth is broken from the gingival margin (gum line) or a tooth where the crown portion is severely decayed or tooth that has not erupted in the mouth (impacted), these teeth are extracted by giving an incision (cut) in the gum and then with the help of an elevator that is inserted in the cut the tooth is removed. In few cases the tooth is broken into pieces and then removed (Sectioning).
Sectioning is the preferred choice in cases of impaction or in cases where the roots are fused together or fused to the bone (Ankylosed tooth).
Surgical extraction if carefully planned and performed, causing as minimum a trauma as possible to the bone and under adequate antibiotic coverage, poses little threat of complications or post extraction infection.